Valuation on Intangible Assets
Intangible asset means an asset that is not in physical nature but have monetary value. Eg – Patents, Copyrights, Brand name, Tradenames, Goodwill and Software.
As per Para21 of INDAS 38 Intangible Assets, Notified by MCA:
An intangible asset should be recognized only when following conditions are satisfied i.e.
a. future economic benefits will be earned by the entity due to holding such intangible asset
b. cost of intangible can be measured through reliable resources.
Otherwise, an expenditure incurred in respect to intangible asset should be recognized in the Profit & Loss account in the financial year in which expense is incurred. However, if both the above conditions are satisfied then it should be recorded as follow:
a. if asset is acquired separately, then acquisition cost.
b. If asset is acquired in business combination or through a government grant, then it should be fair value.
c. If asset is developed internally, then the expenditure incurred in development phase shall be recognition value.
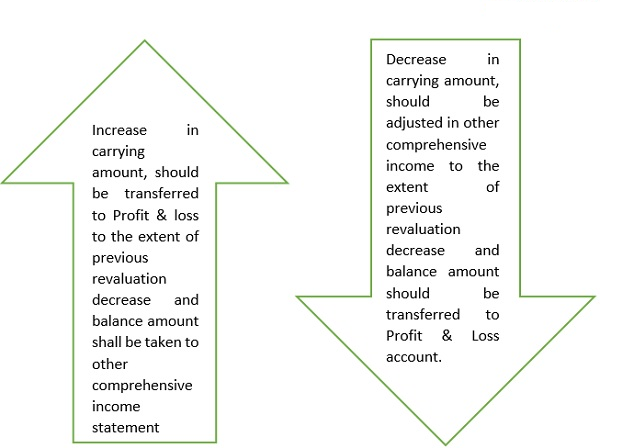
Effects of Revaluation
INDAS 38 provides two types of useful lives for the purpose of Amortization & Impairment and De-recognition.
Definite life – limited period of benefit from the asset to the entity. Under this, asset is amortized over the life of the asset and tested for impairment when there is indication.
Indefinite Life – No foreseeable period over which asset is expected to generate net cash flows for the entity. It needs to be remembered that here indefinite does not mean infinite. Under this, asset is tested for impairment annually and whenever there is indication, asset may be impaired.
Any gain or loss on derecognition should be transferred to the profit & loss account.
Valuation of Intangible assets as per ICAI valuation standards 302 (ICAI VS 302)
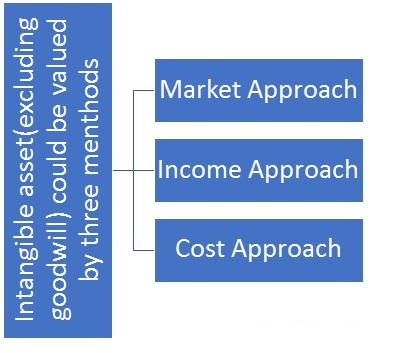
Market Approach – This approach is considered where active market is available for intangible asset and there is sufficient information available about its price in an arm’s length transaction.
Market approach uses prices and other relevant information available by open market transactions involving identical or comparable assets or labilities and group of assets and liabilities, such as business. Market approach is used to value software generally, as comparable market transactions are readily available in the active market.
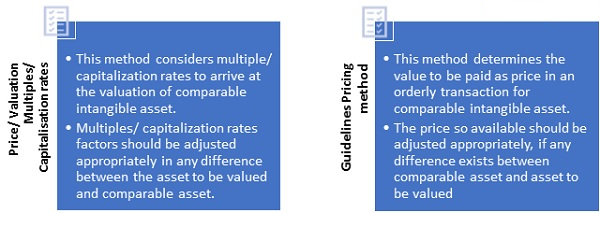
Market approach has further two methods
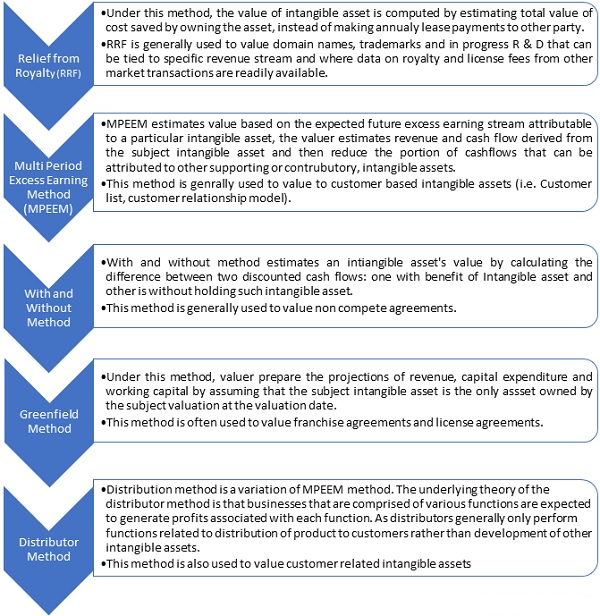
Income approach is the valuation approach that converts expected maintainable future amounts or cash flow into single current amount. Valuation of Intangible asset under income approach is aggregate of present value of expected cash flows or future cost saving by the owner through owning the asset or through license. Expected cash flows or cost saving should be adjusted with the respective expenses and then discounted to compute the present value.
Some of the common following valuation methods under Income approach
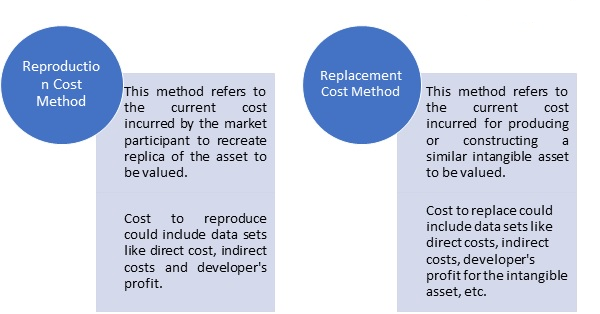
Cost Approach is a valuation approach that reflects the amount that would be required currently to replace the service capacity of an asset.
Valuation of intangible asset using the cost approach is based on the principal rule of substitution i.e., the amount that will be required to create a new similar intangible asset as adjusted for any depreciation becomes the value of intangible asset to be valued.
Cost method is commonly used to value acquired or internally generated intangible assets like software, technology, assembled workforce, etc. Also, cost approach is generally adopted when market and income approach cannot be applied.
Cost method has further following two approaches
There is always a question on which method should be preferred while valuing intangibles given that many methods can be used for valuing intangible assets. The following framework may be useful.


